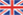
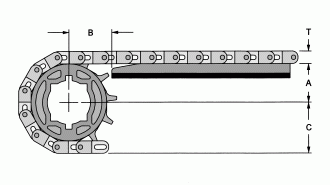
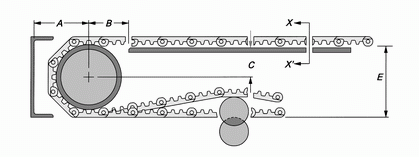
Basic Dimension
The design of the conveyor system are divided into 4 major parts which are belt, drive / Idle part, supporting structure and drive method. The belt structure has been outlined at previous section. The other 3 parts will explain below with details:
Section X-X’
D : 1-10mm
The dimension of belt will have a variation because of temperature change. Please refer to the chapter of Thermal Expansion Calculation to confirm the design dimension.
Dimension Table
|
Unit : mm
|
|
Sprocket
|
A
|
B(min)
|
C(max)
|
T
|
K
|
HW
|
S-HW
|
PD
|
RH
|
SH
|
Acetal
|
SUS304
|
|
Series 100
|
8T
|
57
|
65
|
70
|
16
|
7X7
|
38
|
34
|
133
|
45.5
|
38.5
|
●
|
●
|
|
10T
|
72
|
82
|
86
|
|
164
|
|
●
|
|
12T
|
88
|
100
|
103
|
38
|
196
|
●
|
●
|
|
16T
|
121
|
132
|
136
|
|
260
|
|
●
|
|
Series 200
|
8T
|
27
|
33
|
35
|
10
|
6X6
|
22
|
7.5
|
64
|
30.5
|
- -
|
●
|
●
|
|
12T
|
43
|
50
|
52
|
7X7
|
38
|
34
|
98
|
45.5
|
38.5
|
●
|
●
|
|
20T
|
76
|
83
|
85
|
|
163
|
|
●
|
|
Series 300
|
8T
|
51
|
62
|
63
|
15
|
7X7
|
12
|
- -
|
120
|
45.5
|
38.5
|
●
|
●
|
|
12T
|
80
|
82
|
94
|
- -
|
185
|
●
|
●
|
|
Series 400
|
8T
|
10
|
14
|
16
|
7
|
3X3
|
- -
|
4
|
26
|
12.5
|
- -
|
|
●
|
|
12T
|
16
|
21
|
22
|
4X4
|
- -
|
38.5
|
25.3
|
- -
|
|
●
|
|
24T
|
35
|
38
|
41
|
8X8
|
25.5
|
12
|
76.5
|
45.5
|
38.5
|
●
|
●
|
|
Series 500
|
12T
|
41
|
52
|
53
|
13
|
7X7
|
10.5
|
5
|
93
|
45.5
|
38.5
|
●
|
●
|
|
24T
|
89
|
100
|
102
|
190
|
●
|
●
|
Pay for manufacturing particular dimensions of Stainless Steel Sprocket Bore is acceptable.
S-HW is the hub dimension of Stainless Steel Drive Sprocket.
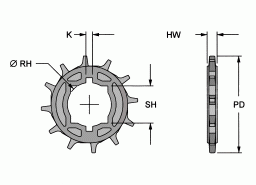
Center Drive
Minimum Diameter of Idler Roller - D ( Return Way )
|
Unit : mm
|
|
Series
|
100
|
200
|
300
|
400
|
500
|
|
íD (min.)
|
180
|
150
|
180
|
60
|
150
|
Idler Roller
Section X-X’

The dimension of belt will have a variation because of temperature change. Please refer to Expansion Calculation in left menu to confirm the design dimension.
Dimension Table
|
Unit : mm
|
|
Roller Diameter ( min.)
|
A ( min. )
|
B ( min. )
|
C ( max. )
|
D ( min. )
|
E ( max. )
|
|
Series 100
|
104
|
76 【 1
|
38 【 2
|
57
|
3
|
114
|
|
Series 200
|
54
|
40 【 1
|
18 【 2
|
27
|
3
|
59
|
|
Series 300
|
102
|
69 【 1
|
34 【 2
|
51
|
3
|
117
|
|
Series 400
|
20
|
19 【 1
|
7 【 2
|
10
|
2
|
27
|
|
Series 500
|
82
|
56 【 1
|
27 【 2
|
41
|
3
|
95
|
Precision
|
Unit : mm
|
|
Conveyor Size
( Width )
|
Length
|
|
≥ 5M
|
≥ 10M
|
≥ 15M
|
≥ 20M
|
≥ 25M
|
≥ 30M
|
|
≥ 350
|
± 2.0
|
± 2.5
|
± 2.5
|
± 3.0
|
± 3.0
|
± 3.5
|
|
≥ 500
|
± 2.5
|
± 2.5
|
± 2.5
|
± 3.0
|
± 3.5
|
± 4.0
|
|
≥ 650
|
± 2.5
|
± 2.5
|
± 3.0
|
± 3.5
|
± 4.0
|
± 4.5
|
|
≥ 800
|
± 2.5
|
± 3.0
|
± 3.5
|
± 4.0
|
± 4.5
|
± 5.0
|
|
≥ 1000
|
± 3.0
|
± 3.5
|
± 4.0
|
± 4.5
|
± 5.0
|
± 5.5
|
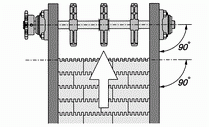
When the conveyor is designed to adopt HONGSBELT modular plastic conveyor belt with steel links, the angle between drive shaft and conveyor structure should be accurate in perpendicular, to prevent the deformation of stainless steel rods that would cause the belt to be damaged because of it does not operate in parallel.
Expansion Calculation
Most of objects have the phenomenon of thermal expansion and contraction. Therefore, the phenomenon of thermal expansion and contraction of material caused by temperature change must be considered while designing the conveyor system.
Temperature Rang of Belt Materials
|
Belt Materials
|
|
Polypropylene |
Polyethylene |
NYLON
|
Actel
|
|
Temperature Range (°C)
|
|
1~100
|
-60~60
|
-30~150
|
-40~60
|
The table above is the standard temperature range of plastic materials for general application. For the standard temperature range of HONGSBELT belt materials, please refer to Basic Data unit in Products Chapter.
Expansion & Contraction Comparison Table - e
|
Unit : mm / M / °C
|
|
Belt Materials
|
Material Used for Supporting
|
Metal
|
|
Polyproeylene
|
Polyethylene
|
NYLON
|
Actel
|
Teflon
|
HDPE & UHMW
|
Carbon Steel
|
Aluminum Alloy
|
Stainless Steel
|
|
73°C~30°C
|
30°C~99°C
|
|
0.12
|
0.23
|
0.07
|
0.09
|
0.12
|
0.14
|
0.18
|
0.01
|
0.02
|
0.01
|
Expansion & Contraction Calculation Formula
Both length and width of belt will be affected by the ambient temperature change, such as belt will extend when temperature increases and contract when temperature decreases; this part should be considered with a deliberate calculation while designing the conveyor system. The calculation formula of dimension variation are as follow.
|
FORMULA :
|
TC = LI × ( To - TI )× e
|
|
Symbol
|
Definition
|
Unit
|
|
TC
|
Dimension change
|
mm
|
|
TCL
|
Length after temperature change
|
mm
|
|
TCW
|
Width after temperature change
|
mm
|
|
LI
|
Dimension at initial temperature
|
M
|
|
To
|
Operating temperature
|
°C
|
|
TI
|
Initial temperature
|
°C
|
|
Example 1:
|
The conveyor belt in P.P. material with the dimension in 18.3m for the length and 3.0m for belt width, start form the operating temperature 21℃. What will be the result of the belt length and width at operating temperature increase up to 45°C ?
|
|
|
TCL = 18.3 × ( 45 - 21 ) × 0.124 = 54.5 ( mm )
TCW = 3 × ( 45 - 21 ) × 0.124 = 8.9 ( mm )
|
|
|
From the calculation result, we know that the length of belt will increase approximately up to 55mm and the width of belt may increase nearly 9 mm under temperature range 21 ~ 45°C.
|
|
|
|
|
Example 2:
|
The conveyor belt in P.E. material with the dimension in 18.3m for the length and 0.8m for belt width, start form the operating temperature 10℃. What will be the result of the belt length and width at operating temperature increase down to -40°C ?
|
|
|
TCL = 18.3 × ( - 40 - 10 ) × 0.231 = - 211.36 ( mm )
TCW = 0.8 × ( - 40 - 10 ) × 0.231 = - 9.24 ( mm )
|
|
|
From the calculation result, we know that the length of belt will reduce approximately 211.36 mm and the width of belt may reduce nearly 9.24mm, under temperature range 10 ~ -40°C.
|
Prefix V
|
Chemical Name
|
Temperature
Condition
|
Belt Materials
|
|
ACETAL
|
NYLON
|
P . E .
|
P . P .
|
|
Vinegar Still Agitated Aerated
|
21°C
|
N
|
|
O
|
O
|
O = OK, N = NO